SAS designed JMP to perform dynamic, visual data exploration and statistical discovery.
RBI, LLC fully automates any JMP Process using JSL (JMP Scripting Language)
We Can Automate
JMP Analysis & Graphing Automation – any JMP Analysis or Charting platform with customized parameters for your application
Custom Report Creation – Multiple statistical analysis tests and charts compiled in customized displays. We can hide almost any element in any JMP Platform display and arrange them to your specifications integrating custom images and text.
High DPI PDF Output – Not all of JMP's platforms are designed for high DPI output. Rothenberg Industries will ensure your report is designed for high DPI PDF generation from the onset
Rothenberg Industries, LLC can automate any JMP process or feature using the JMP Scripting Language (JSL):
Six Sigma Manufacturing Control Charts & Reports - including IR, X-bar and R charts with Statistical Process Control (SPC) flagging, Distribution charts with capability analysis (Cp/Cpk) using either customized Spec Limits or Shewart’s limit definition.
Raw Data Import Automation – Import your data from Microsoft SQL Server, SQL Azure, AWS or any other cloud host. Microsoft Access or Excel, CSV, Flat & Text Files, or via any other data source with a compatible ODBC driver.
Data Manipulation – Merge, Sort and/or Filter data-sets into an optimal format for statistical analysis. Apply custom Formulas.
JMP Analysis & Graphing Automation – any JMP Analysis or Charting platform with customized parameters for your application
Custom Report Creation – Multiple statistical analysis tests and charts compiled in customized displays. We can hide almost any element in any JMP Platform display and arrange them to your specifications integrating custom images and text.
High DPI PDF Output – Not all of JMP's platforms are designed for high DPI output. Rothenberg Industries will ensure your report is designed for high DPI PDF generation from the onset
Design of Experiments (DOE) Consultation
Gage R&R Measurement System Analysis
ANOVA & Multi Variable Regression Analysis
WE OFFER SERVICES FROM A CONSULTING CONFERENCE CALL TO DOOR-TO-DOOR TURNKEY SOLUTIONS. MANY APPLICATIONS CAN BE DEVELOPED AND IMPROVING YOUR BUSINESS EFFICIENCY IN UNDER TWO WEEKS.
case studies
Here are some examples of what can be accomplished with JMP JSL
JMP Automated SPC Report with Capability Analysis
Data Visualization statistics, data-visualization, mechanical-engineering, manufacturing, sas
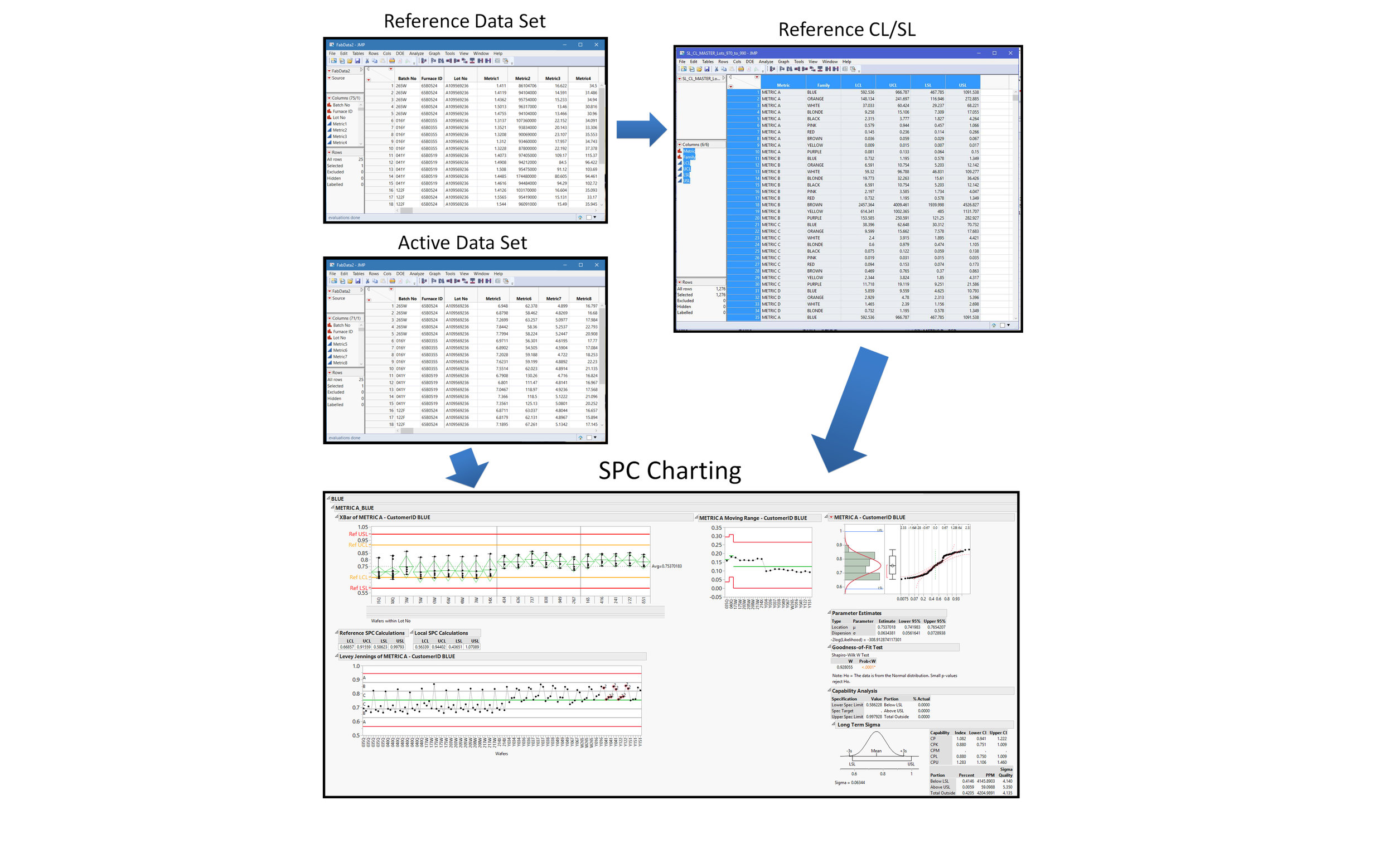
A two-step statistical analysis process that generates control & spec limits from a user defined data set and then generates an SPC report from another user defined data set using reference limits generated by the first step. The first script prompts the user for a lot range and calculates the control and spec limits defined by +/-3 and 5 sigma respectively. The first “CL/SL Generator” script can delimit the data by a variable number of levels, by family, by lot, etc. The script then saves these limits into a master table whose root path is predefined by the user. The second “SPC Analysis” script prompts the user for a lot range of data to analyze and import any reference CL/SL set as predefined by the user. A report is generated that includes an X-bar Variability Chart with imported reference limits by default and locally defined limits if there is not matching metric in the reference CL/SL set. The report also includes an X-bar moving Range Chart and a Levey Jennings SPC chart that analyzes the stability and predictability of a pre-established process metric. The Levey Jennings SPC chart flags out of control occurrences as defined by the WECO rules and using +/-3 local Sigma for the control limits instead of Shewart’s original control limit definition. The report also includes a distribution analysis to test for normality and a capability analysis used to assess whether the process is statistically able to meet the reference specification limits.
SPC/Cp Report *All Data Fabricated


Process Flow
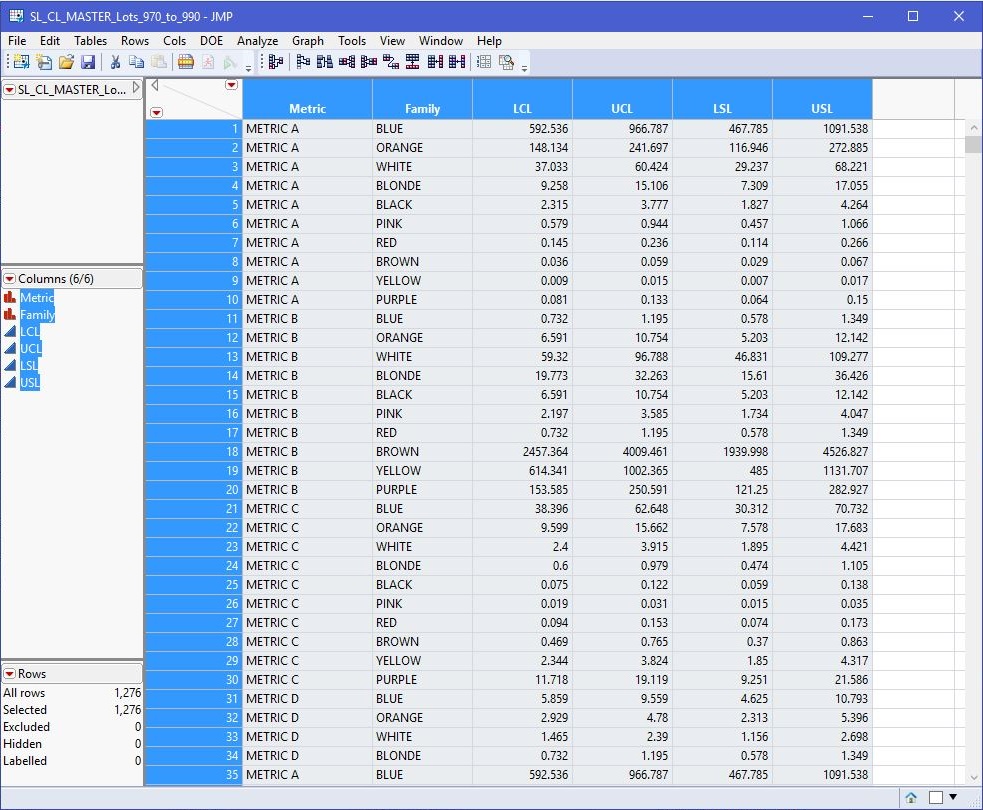
Control Limit & Spec Limit Table calculated by generator script
Essential Statistical review
We will review several introductory concepts that are fundamental to analytical statistics and are crucial when interpreting results and drawing conclusions from your emperical data.

The Population and Sample
Inferential statistics makes generalizations or inferences from your data to a larger set of data, such as a population, based on probability theory. Descriptive statistics are used to organize, summarize and focus on the main characteristics of your sample. Summarizing your data in such a manner also makes it more usable.
There is a process involved in inferential statistical analysis:
1) Identify the population or application
2) Draw a representative sample
3) Compute sample statistics to describe the sample
4) Use the sample information to make inferences about the population.


Statistical Definitions

The central limit theorem is used to satisfy the assumption of normality for confidence intervals. Where the normal distribution and its confidence intervals are shown below


Rothenberg Industries, LLC automates repetitive tasks requiring importing & manipulating data, statistical analysis or report generation (PDF) using the JMP Scripting Language (JSL)

JMP Report Generator with GUI and PDF Output
Data Visualization statistics, data-visualization, mechanical-engineering, manufacturing, sas, gui
We were contacted by a client to design a JMP JSL script that includes a GUI to specify reporting parameters, generate a JMP report and saving the report window as a PDF. Our client requested us to import their manufacturing metrics and limits from several Microsoft SQL tables, create a custom report of distribution & individual run charts with spec and control limits with a capability analysis (Cp & Cpk).
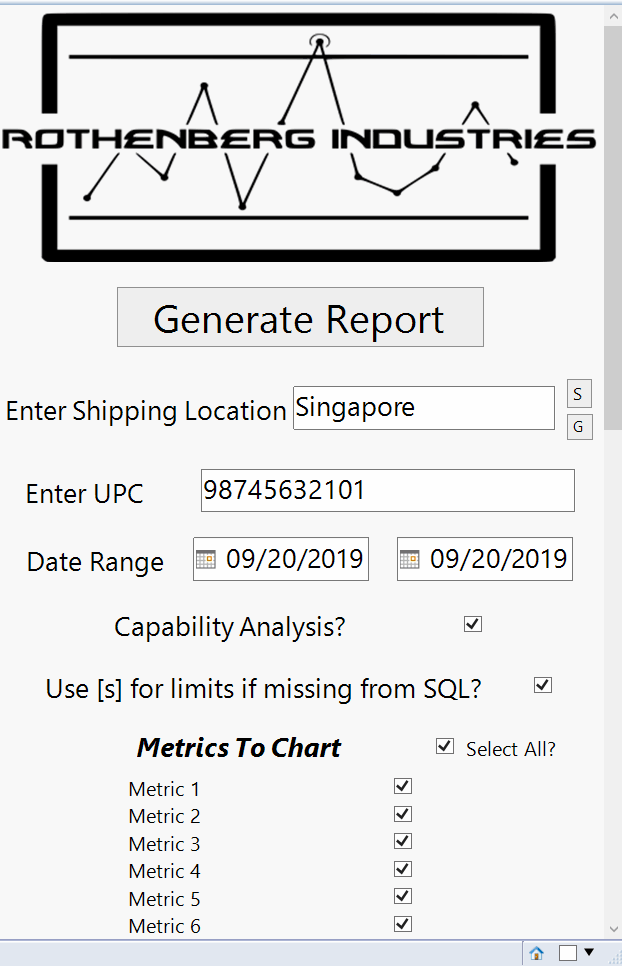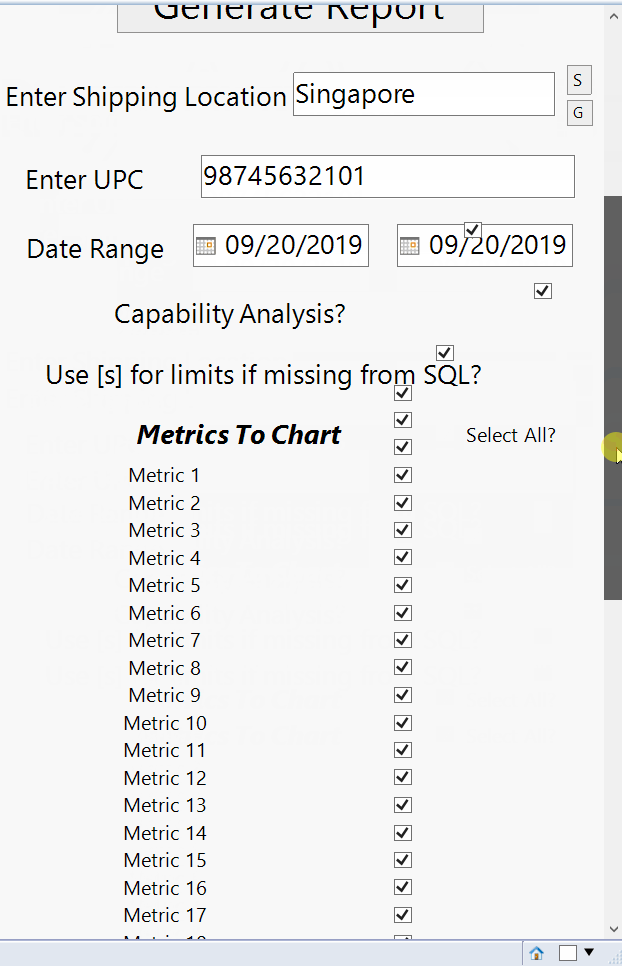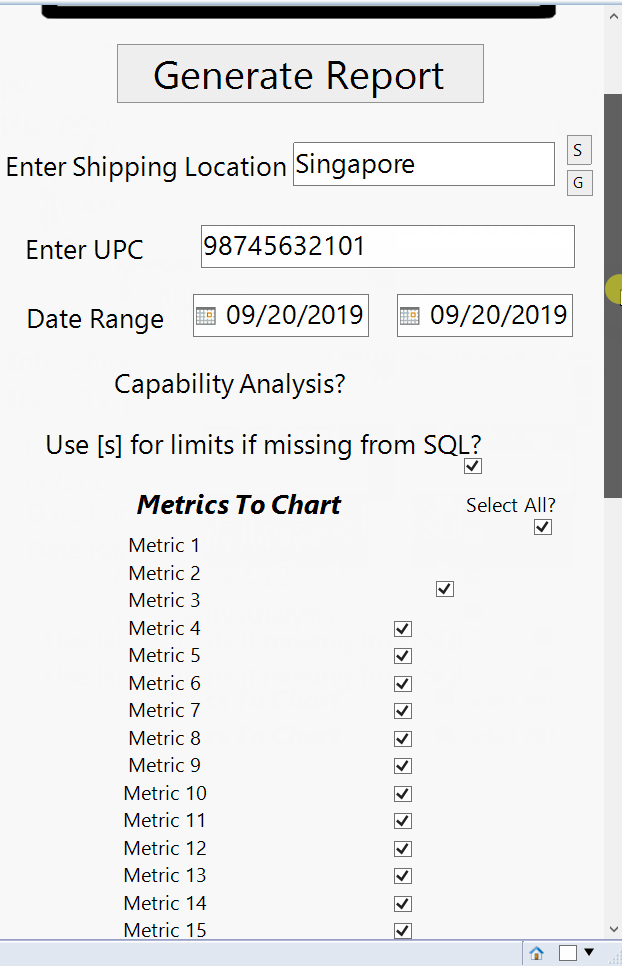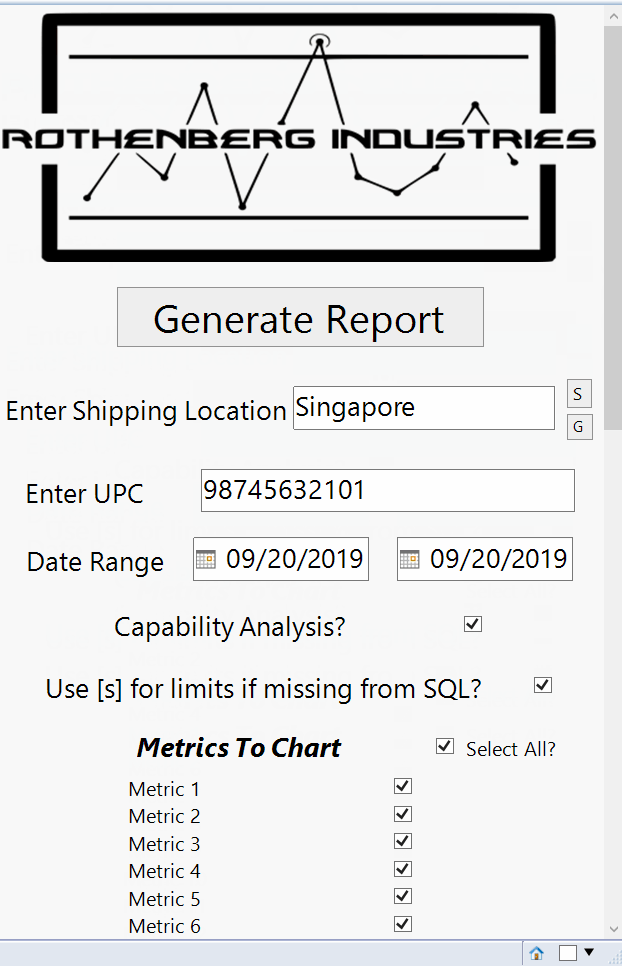
JMP GUI - Operator enters UPC, dates & metrics to report
Custom Report GUI
Upon running the script, the initial GUI window will display as shown. The user has the option to include a capability analysis in the report to determine if the process is statistically capable of meeting the respective specification limits. The user also has the option to use +/-3 and 5 sigma as the spec and control limits respectively instead of the default option that queries the predefined limits from a Microsoft SQL Server Table.
JMP Report
Upon selecting ‘Generate Report’ the script will create individual run and distribution charts for the respective metrics using the designated reference limits.A capability analysis is also reported if selected to determine if the process is statistically capable of meeting the reference specification limits.
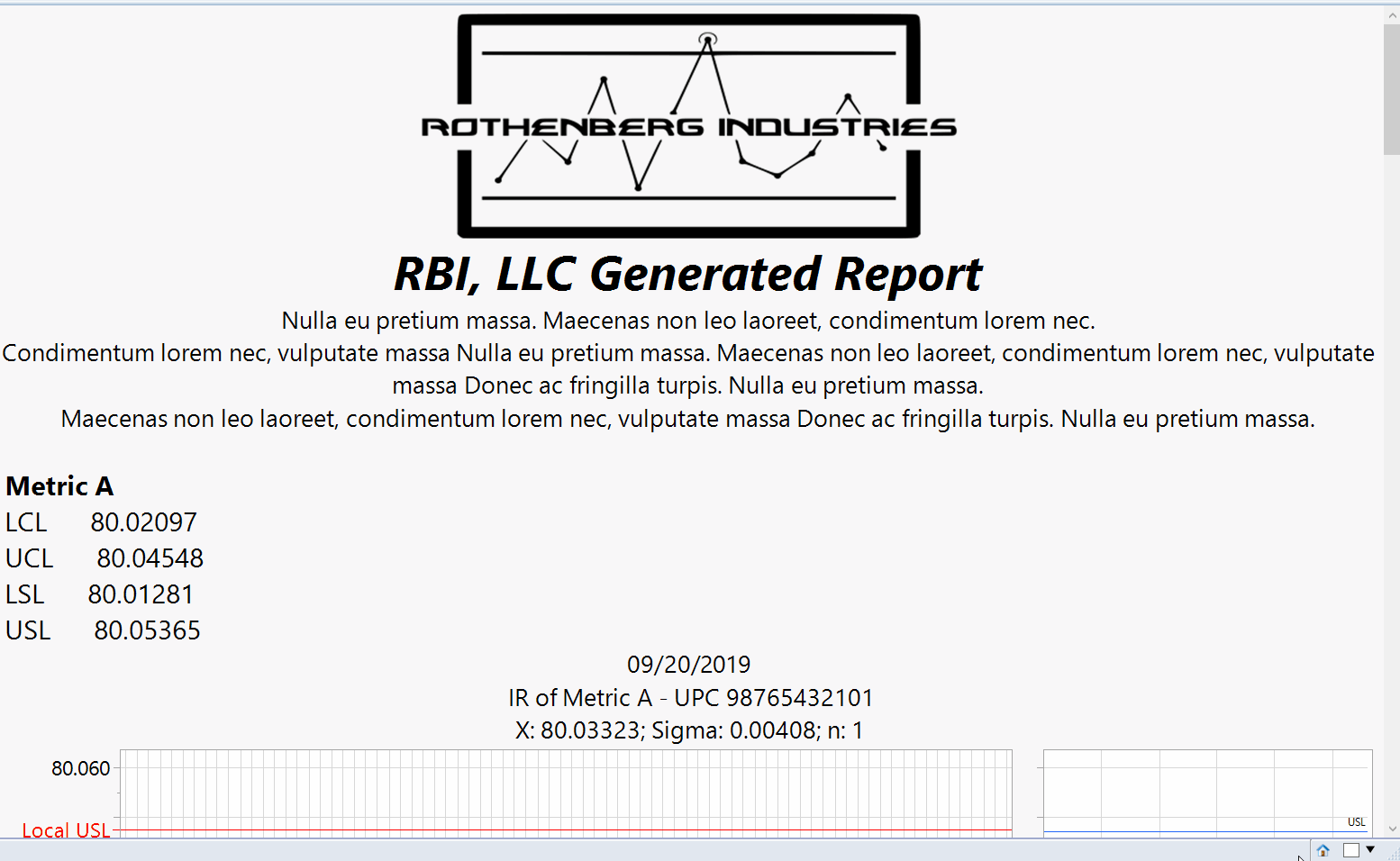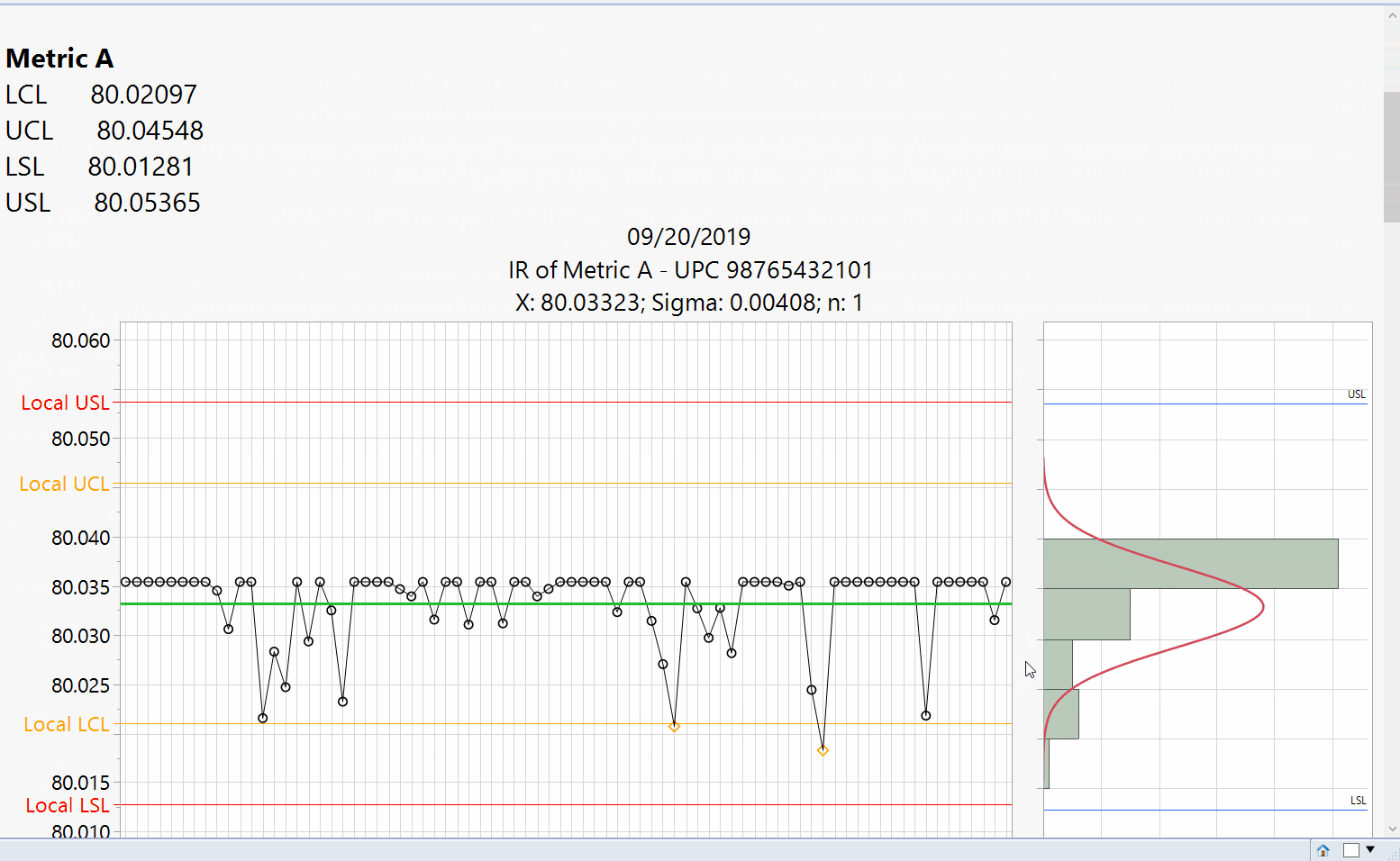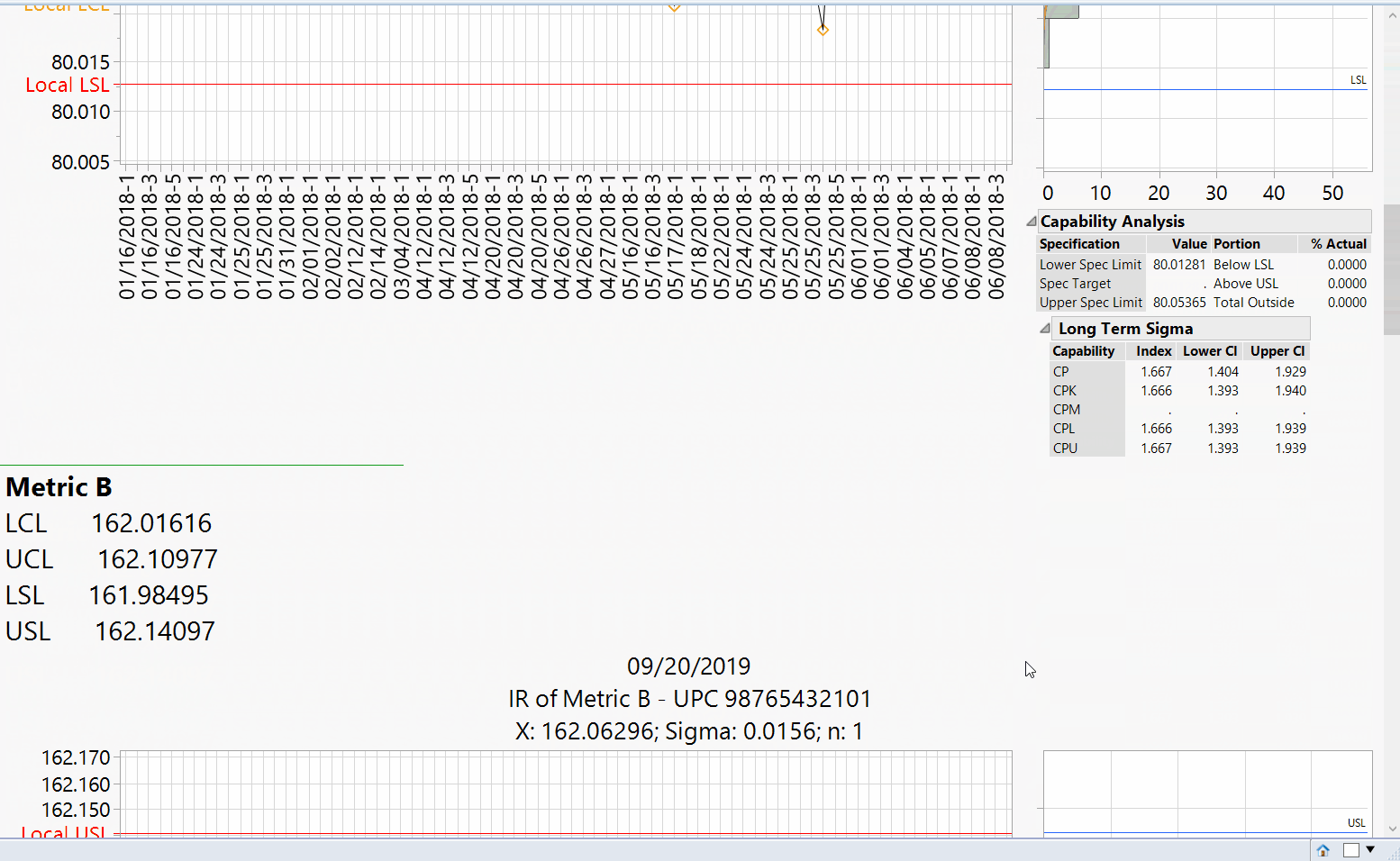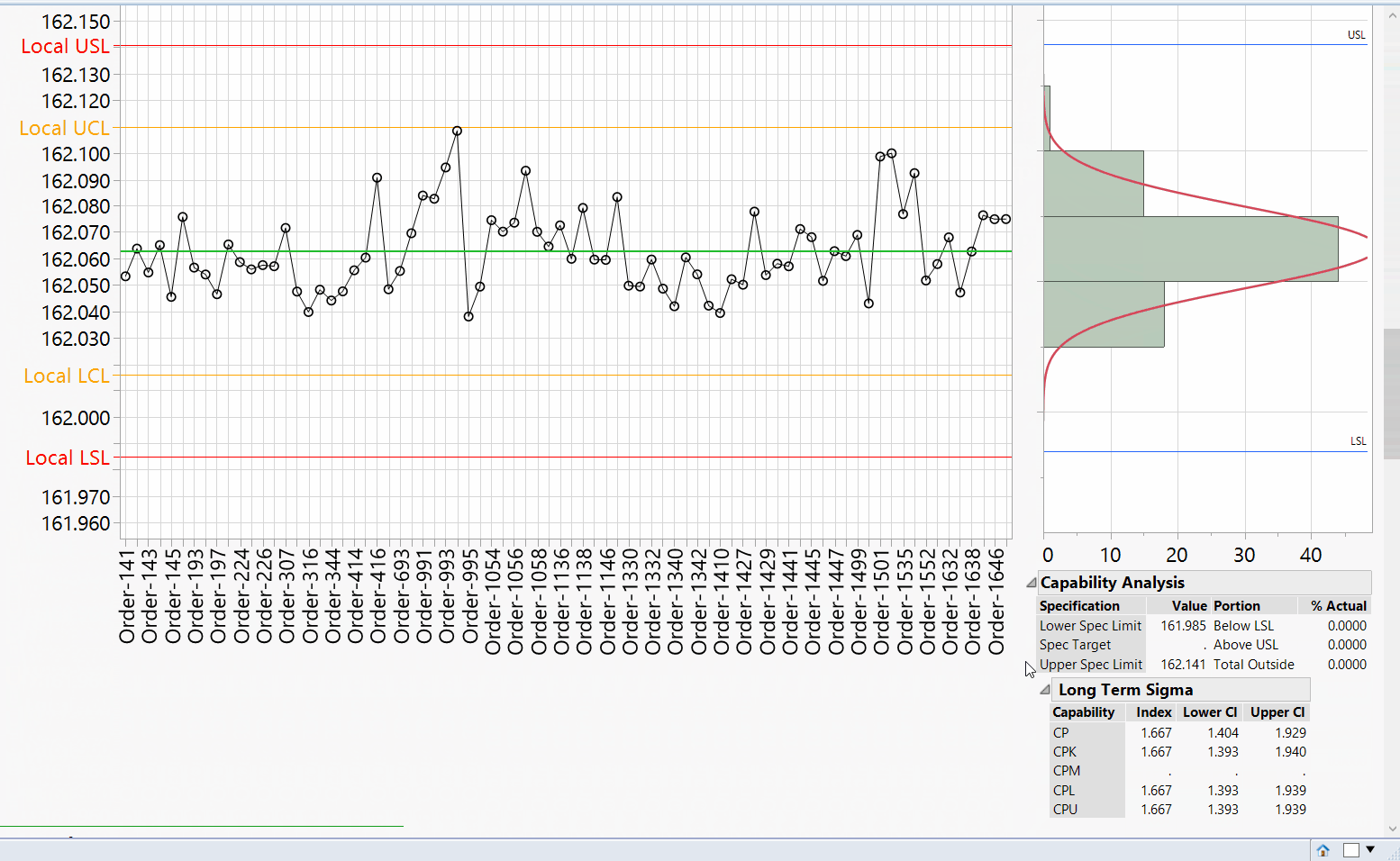
JMP Generated Report
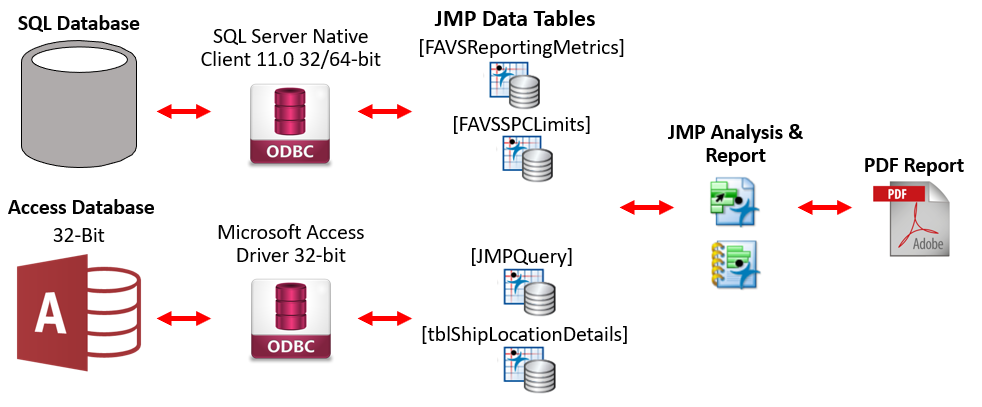
Process Flow
First, we created a JMP JSL script that imports data from both the client’s SQL & Access database into JMP data tables via their respective ODBC drivers. The script then performs various data manipulations, creates the statistical charts, constructs a JMP Report Window and then exports that window into a PDF file.